No.15001 Cases where inheritance tax is imposed
1 Framework of inheritance tax
If the total value of properties acquired by inheritance or bequest and properties acquired under taxation by settlement at the time of inheritance (after subtracting the amount of debt, etc., and adding the value of properties donated within three years before commencement of inheritance) exceeded the amount of basic exemption, inheritance tax is imposed on the excess amount (total taxable estate).
In this case, a declaration and payment of inheritance tax is required within ten months from the day following the day when the death of the decedent (Note) was notified.
(Note) Decedent refers to the deceased person.
* By the tax reform in fiscal year 2023, the system has been revised including extension of the scope of the donated properties from within 3 years to 7 years before the beginning of the inheritance for a person who acquired property by inheritance, bequest, or donation under the taxation for settlement at the time of inheritance to add the donated property to the property acquired by inheritance, etc. (limited to the donation under the taxation for calendar year on and after January 1, 2024).
2 The amount of basic exemption and net estate
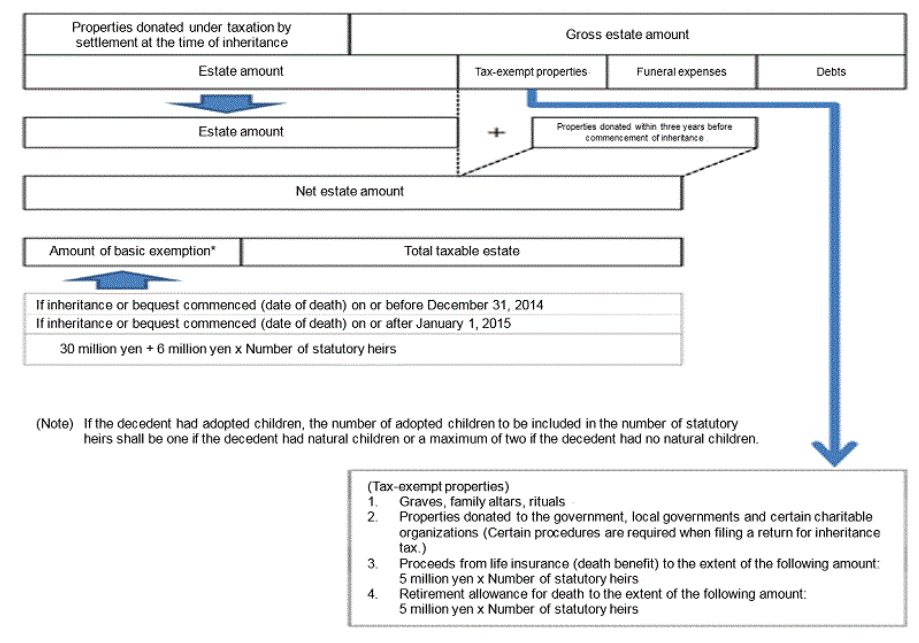
If the net estate amount exceeds the amount of basic exemption, inheritance tax will be imposed, so a declaration and payment of inheritance tax need to be made.
Net estate amount represents the total amount of gross estate amount and properties donated under taxation by settlement at the time of inheritance, after subtracting the tax-exempt properties, funeral expenses and debts and adding the properties donated within three years before commencement of inheritance, as shown in the above diagram.
3 People with obligation to pay inheritance tax and taxable properties
People with obligation to pay inheritance tax and scope of taxable properties are as follows:
| People with obligation to pay inheritance tax and scope of taxable properties | |
|---|---|
| People subject to inheritance tax | Scope of taxable properties |
|
(1) A person who acquires properties by inheritance or bequest and has an address in Japan at the time of inheritance. (This does not apply if the person is a temporary resident and the decedent is a foreigner or non-resident.) |
All properties acquired |
|
(2) A person who acquires properties by inheritance or bequest and does not have an address in Japan at the time of inheritance, in addition to the following: (a) The person has Japanese citizenship at the time of inheritance and one of the following applies: (ⅰ) The person had an address in Japan within the last ten years before the commencement of inheritance; or (ⅱ) The person did not have an address in Japan within the last ten years before the commencement of inheritance (excluding the case where the decedent is a foreigner or non-resident). (b) The person does not have Japanese citizenship at the time of inheritance (excluding the case where the decedent is a foreigner, non-resident or non-resident foreigner). |
All properties acquired |
|
(3) A person who acquires properties in Japan by inheritance or bequest and has an address in Japan at the time of inheritance (excluding those who fall under (1) above). |
Properties in Japan |
|
(4) A person who acquires properties in Japan by inheritance or bequest and does not have an address in Japan at the time of inheritance (excluding those who fall under (2) above). |
Properties in Japan |
|
(5) A person who does not fall under any of (1) to (4) above, but acquires properties by donation, for which taxation by settlement at the time of inheritance is applicable. |
Properties under taxation by settlement at the time of inheritance |
(Notes)
| 1. | A "temporary resident" refers to a person who has a status of residence (i.e. a status of residence as listed in the above column of the Attached Table 1 of the Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act) at the time of commencement of inheritance, and had an address in Japan for a total of ten years or less within the last 15 years before the commencement of inheritance. |
| 2. | A "decedent who is a foreigner" refers to a decedent who has a status of residence at the time of commencement of inheritance, and had an address in Japan. |
| 3. | A "decedent who is a non-resident" refers to a decedent who does not have an address in Japan at the time of commencement of inheritance, and who falls under either of the following categories: (1) a person who had an address in Japan any time within the last ten years before the commencement of inheritance, and who did not keep their Japanese citizenship any time within that period; or (2) a person who did not have an address in Japan within the last ten years before the commencement of inheritance. |
| 4. | A "non-resident foreigner" refers to a person who did not keep his/her address in Japan or Japanese citizenship continuously from April 1, 2017 through the time of inheritance or bequest. |
| 5. | Association or foundation without legal personality, or corporation in which the equity interest is not specified may be subject to inheritance tax. |
| 6. | With regard to (1) and (2) in the table above, the rules may be different if you had applied for the "special provisions to allow postponement of tax payment for exit tax system" after July 1, 2015. |
- Consultation service for national tax is available at the Phone Consultation Center of the Regional Taxation Bureaus. Please take a look at "IF YOU NEED FURTHER INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT" and try the phone consultation service.