No.12007-2 Foreign tax credit for non-residents
1 What is foreign tax credit for non-residents?
If a non-resident with a permanent establishment in Japan becomes liable to pay foreign income tax in the year, which is imposed on the income attributable to the permanent establishment under foreign laws and regulations and equivalent to Japanese income tax (hereinafter referred to as “foreign income tax”) , the amount of such foreign income tax shall be credited against Japanese income tax for the year, up to the amount calculated by the formula (1) below (hereinafter referred to as "credit limit for income tax").
(1) Credit limit for income tax = Amount of income tax on the income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year × (Adjusted amount of foreign income for the year / Total amount of income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year)
Furthermore, if the amount of foreign income tax for the year exceeds that of credit limit for income tax, the amount of such excess shall be credited against the special income tax for reconstruction for the year, up to the amount calculated by the formula (2) below (hereinafter referred to as "credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction").
(2) Credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction = Amount of special income tax for reconstruction on the income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year × (Adjusted amount of foreign income for the year / Total amount of income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year)
| (Note 1)“Income attributable to the permanent establishment” means the following income: |
(a) Income which might be attributed to the permanent establishment, if it were an entity engaged in business independently from the non-resident who carries out business through that establishment (hereinafter referred to as "Income to be attributed to a permanent establishment"). |
(b) Prescribed distribution of profits arising from business conducted through a permanent establishment based on a partnership contract. |
| (Note 2)"Amount of income tax on the income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year" means the amount of income tax calculated without applying the provisions of Article 165-6 of the Income Tax Act (Foreign Tax Credit for Non-resident) after applying tax credits such as special credit for donation to public interest incorporated association, etc. (excluding the amount of additions to tax) to the amount of income tax for the relevant year as an amount of income tax with respect to income attributable to the permanent establishment which is calculated in accordance with the provisions of Articles 89 (tax rates) to 92 (dividend tax credits) of the Income Tax Act and the provisions of Article 165-5-3 (credit for the adjusted amount equivalent to foreign taxes at the time of distribution for non-residents) according to under the provisions of Article 165, paragraph 1 of the same Act based on the “income attributable to the permanent establishment” (Calculation of the Tax Base and Amount of Income Taxes Imposed on Aggregate Income of Nonresidents), the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 8-4, paragraph 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Dividend Income, etc. Related to Listed Shares, etc.), the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 31, paragraph 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Long-term Capital Gains), the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 32, paragraphs 1 or 2 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Short-term Capital Gains), the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 37-10, paragraph 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Capital Gains Related to Common Shares, etc.), the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 37-11, Paragraph 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Capital Gains Related to Listed Shares, etc.), and the amount of income tax pursuant to the provisions of Article 41-14, paragraph 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Taxation (Special Provisions for Taxation on Miscellaneous Income, etc. Related to Futures Transactions). |
| (Note 3)"Total amount of income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year" means the amount of “income attributable to the permanent establishment” for the year, but not applying the provisions of carry-over for net loss or casualty loss. |
| (Note 4)"Adjusted amount of foreign income for the year" means the amount of foreign income for the year, but not applying the provisions of carry-over for net loss or casualty loss. In the case where the amount of foreign income for the year exceeds the “total amount of income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year”, it shall be equal to the “total amount of income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year”. |
| (Note 5)"Amount of special income tax for reconstruction on the income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year" means the amount after applying the credit for the amount equivalent to foreign taxes adjusted upon distribution related to the special income tax for reconstruction on the income attributable to the permanent establishment to the amount obtained by multiplying the base income tax (equal to the “amount of income tax on the income attributable to the permanent establishment for the year(the amount without applying the credit for the amount equivalent to foreign taxes adjusted upon distribution related to the income attributable to the permanent establishment and foreign tax credit)) by the rate of 2.1%. |
2 Scope of deductible foreign income tax for non-residents
Taxes corresponding to foreign income tax
“Foreign income tax” means a tax that is imposed on income of an individual as a tax base under foreign the law and regulations by a foreign government or its local authorities, including the following:
- (1) An excess income tax or a similar tax that is imposed on a specific part of income of an individual as a tax base.
- (2) A surtax that is imposed on the whole or specific part of income of an individual as a tax base.
- (3) A tax that is imposed on the amount of earnings or its equivalent instead of the amount of income as a tax base, with regard to the specific type of income of an individual, for the convenience of tax collection, which is categorized in the same kind of tax that is imposed on income of an individual as a tax base.
- (4) A tax that is imposed on the amount of earnings or its equivalent with regard to the specific type of income of an individual as a tax base, which is substituted for the tax that is imposed on the income as a tax base.
Taxes excluded from foreign income tax
Even if a tax is imposed by a foreign government or its local authorities, the followings are excluded from foreign income tax:
- (1) A tax after the payment of which the whole or part thereof is refundable upon the request by a taxpayer.
- (2) A tax of which a grace period for payment can be decided arbitrarily by a taxpayer.
- (3) Certain part of a tax the tax rate of which applicable to a taxpayer is chosen from various tax rate options by the agreement between the taxpayer and a foreign government or its local authorities or those who are authorized to make that agreement.
- (4) A tax that is imposed incidental to foreign income taxes, and the like.
Foreign income tax amount for which you cannot take a credit
The following amounts of foreign income tax are not deductible for foreign tax credit.
- (1) The amount of foreign income tax imposed on income derived from prescribed transactions as not to be considered as arm’s-length.
- (2) In the case where foreign income tax imposed in countries other than the country of residence (hereinafter referred to as the "third country") of the earner who is a non-resident in Japan, the amount equivalent to the portion exceeding the prescribed amount as the limit that might be imposed by the third country, or the amount equivalent to the exempted amount, according to the provision of the tax treaty if it were applied to the income as a tax base of such foreign income tax.
- (3) In the case where foreign income tax imposed in any third country, and if the income, as a tax base of that foreign income tax, were earned by a resident of Japan and were taxable in the prescribed foreign country which is eligible for “Mutual Exemption Law for Income of Foreign Resident,etc.”, the amount equivalent to the portion to be reduced, or to be exempted from taxation, on the same conditions to be applied to the qualified domestic source income earned by a “foreign resident” as prescribed in the provision of the law above.
- (4) In the case where foreign income tax imposed in any third country, and if the income, as a tax base of that foreign income tax, were earned by a resident of Japan and were taxable in the prescribed foreign country which is eligible for “Mutual Exemption Law for Income of Foreign Resident, etc.”, the amount equivalent to the portion to be reduced, or to be exempted from taxation, on the same conditions to be applied to the qualified domestic source income earned by a “foreign resident” as prescribed in the provision of the law above.
3 What is the amount of foreign income?
“Amount of foreign income” means the amount of “Income to be attributed to a permanent establishment of a non-resident” which falls under the following kinds of foreign source income. “Adjusted amount of foreign income for the year” is equal to the “amount of foreign income” for the year without applying the deductions of carried-over net loss and casualty loss, which is an element when in calculation of “credit limit for income tax” for the year.
It should be noted that, with regard to a non-resident to whom a tax treaty is applicable, if the tax treaty contains provisions on foreign source income which differ from the followings the foreign source income shall be governed by the tax treaty to the extent that such different provisions are concerned.
(1) Income arising from the use or holdings of assets located outside Japan.
(2) Income arising from the transfers of assets located outside Japan.
(3)Consideration received by a person who conducts prescribed business for which the main activity is to provide personal services outside Japan, for the provision of the said personal services.
(4) Consideration for the lease of real property located outside Japan, any right on real property located outside Japan; or quarrying right granted outside Japan, establishment of mining lease rights outside Japan, or lease of vessels or aircraft to non-residents or foreign corporations.
(5) Interest, etc. prescribed in Article 23, paragraph 1 of the Income Tax Act and those equivalent thereto, as set forth in the following:
( ) ) |
Interest on foreign government bonds or municipal bonds, or bonds issued by foreign corporations; |
( ) ) |
Interest on deposits or savings deposited with business offices located outside japan; |
( ) ) |
Distribution of revenue from joint operation trusts or any other trusts equivalent thereto, bond investment trusts, or publicly offered bond management investment trusts or any other trusts equivalent thereto, which have been entrusted with business offices located outside Japan. |
(6) Dividends, etc. prescribed in Article 24, paragraph 1 of the Income Tax Act and any money equivalent thereto, as set forth in the following:
( ) ) |
Dividends of surplus, dividends of profits, distributions of surplus, distribution of money or interest on funds and equivalent thereto, which are received from foreign corporations; |
( ) ) |
Distribution of revenue from investment trusts (excluding bond investment trusts and publicly offered bond management investment trusts and any other trusts equivalent thereto) or specified beneficiary certificate issuance trusts or any other trusts equivalent thereto, which have been entrusted with business offices located outside Japan; |
(7) Interest on loans which are provided for persons who carry out operations outside Japan and which pertain to the said operation (including prescribed margin profits arising from buying and selling transactions of bonds with repurchase or resale agreements);
(8) The following royalties or consideration to be received from persons who carry out operations outside Japan, which pertain to the said operations:
( ) ) |
Royalties for rights concerning technology such as industrial property rights, production methods involving special technology or any other rights or methods equivalent thereto; consideration for the transfer thereof; |
( ) ) |
Royalties for copyrights (including rights of publication and neighboring rights, and any other rights equivalent thereto); consideration for the transfer thereof; |
( ) ) |
Royalties for machinery, equipment or other prescribed tools. |
(9) Prescribed monetary awards for advertisement of business conducted outside Japan.
(10) Pension to be received based on contracts for a pension, such as an insurance contract concluded by a foreign insurer, a life insurance company or a non-life insurance company prescribed in Insurance Business Act, which has been concluded via a business office located outside Japan (including surplus to be distributed or rebate to be paid based on such a contract for a pension on or after the date of commencement of payment of the pension, and lump-sum payment to be paid in lieu of pension based on such a contract).
(11) The following compensation money for benefits, interest, profits, or margin profits:
(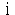 ) ) |
Compensation money for benefits based on a contract for installment savings that have been accepted by a business office located outside Japan; |
(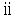 ) ) |
Money equivalent to compensation money for benefits based on a contract as referred to in Article 2, paragraph (4) of the Bank Act, which pertains to money equivalent to the installments that have been accepted by a business office located outside Japan; |
(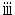 ) ) |
Interest which pertains to a contract equivalent to a prescribed contract concluded based on mortgage securities stipulated in Article 1, paragraph (1) of the Mortgage Securities Act via a business office located outside Japan; |
(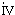 ) ) |
Profits which pertains to a contract for the purchase and sale of a precious metal and the like with a sell-back agreement that has been concluded via a business office located outside Japan; |
(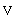 ) ) |
Margin profits arising from deposits or savings in a foreign currency the principal and interest of which are to be paid after conversion into Japanese yen or into a different foreign currency at the rate agreed upon in advance, which pertain to deposits and savings that have been accepted by a business office located outside Japan; |
(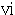 ) ) |
Margin profits, which pertain to a contract equivalent to a payment in full endowment life or non-life insurance contract that has been concluded via a business office located outside Japan. |
(12) Distribution of profits to be received based on a silent partnership agreement and equivalent thereto, for investment in a person who conducts business outside Japan.
(13) In addition to the types of income set forth in the preceding items (1) to (12), income prescribed as income the source of which is located outside Japan:
(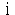 ) ) |
Income such as insurance proceeds, compensation money or compensation for damages and equivalent thereto that is to be received in relation to operations conducted abroad or assets located abroad; |
(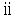 ) ) |
Income arising from assets located abroad donated by a corporation; |
( ) ) |
Income from treasure trove found in a foreign country and income from the acquisition of lost property in a foreign country; |
( ) ) |
Income from bounty, etc. to be performed abroad; |
( ) ) |
Occasional income acquired due to an act performed abroad; |
( ) ) |
Beyond what is listed in the preceding items, income from economic benefits received in relation to operations abroad or assets located abroad. |
4 Calculation of foreign tax credit for non-residents
A non-resident shall deduct the following amount of foreign income tax from the amount of income tax and special income tax for reconstruction for the year that includes the day on which the non-resident becomes liable to pay the foreign income tax (Note):
| (1) | If the amount of foreign income tax does not exceed the credit limit for income tax for the year, the amount of foreign tax credit deductible is equal to the amount of foreign income tax. |
| (2) | If the amount of foreign income tax exceeds the credit limit for income tax for the year, the amount of foreign tax credit deductible is equal to the sum of the credit limit for income tax for the year and the following (a) or (b) whichever is lower: (a) The amount of foreign income tax minus the credit limit for income tax for the year, or (b) Credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction for the year. |
| (Note) | It is also acceptable to take a deduction in the year that includes the day on which the amount of foreign income tax is actually paid as long as a deduction is taken in such a way continuously. |
It is also acceptable to take a deduction in the year which includes the day of payment completed with regard to the fixed foreign income tax as long as the way is taken continuously.
5 Carry-over of foreign tax credit for non-residents
In the following cases, you can additionally deduct prescribed amount as being calculated from the amount of foreign income tax or credit limit for income tax which has been accrued in any of the last three years, against income tax for the year.
(1)If the amount of foreign income tax exceeds the sum of the credit limits
In the case where the foreign income tax to be paid in the year exceeds the sum of the credit limit for income tax, the credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction and the credit limit for local tax for the year (equal to the amount multiplying the credit limit for income tax for the year by 30%), if the amount of credit limit for income tax in any of three years prior to the year which is supposed to be carried over to the year (hereinafter referred to as "credit limit carried over") exists, the excess amount can be credited against income tax for the year, up to the amount of credit limit carried over.
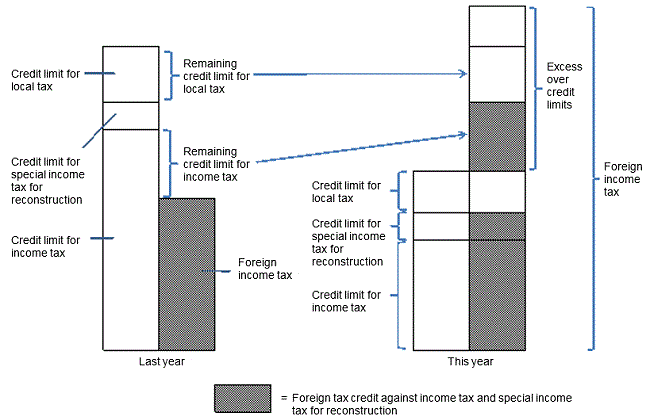
| (Note 1)“Credit limit carried over” is defined as the sum of the remaining credit limits for income tax for any of three years prior to the year, which should be appropriated to the excess over credit limits for the year if each of the remaining credit limits for income tax and the remaining credit limits for local tax for any of three years prior to the year is to be appropriated to the excess over credit limits for the year in chronological order and in order of the remaining credit limit for income tax, the remaining credit limit for local tax as to the same year. |
| (Note 2)“Remaining credit limit for income tax” is defined as the remaining balance of the credit limit for income tax for the year, after deduction of the foreign income tax to be paid in the year in the case where the foreign income tax to be paid in the year is less than the credit limit for income tax for the year. |
| (Note 3)“Remaining credit limit for local tax” is defined as: (i) in the case where the foreign income tax to be paid in the year is equal to or less than the sum of the credit limit for income tax and the credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction for the year, the amount of credit limit for local tax for the year, (ii) in the case where the foreign income tax to be paid in the year exceeds the sum of the credit limit for income tax and the credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction for the year but the excess amount is less than the credit limit for local tax, the remaining balance of the credit limit for local tax for the year after deduction of the excess amount. |
| (Note 4)“Excess over credit limits” is defined as the amount by which the foreign income tax to be paid in the year exceeds the sum of the credit limit for income tax, the credit limit for special income tax for reconstruction and the credit limit for local tax for the year. |
(2) If the amount of foreign income tax is less than the credit limit for income tax
In the case where the foreign income tax to be paid in the year is less than the credit limit for income tax for the year, if the amount of foreign income tax to be paid in any of three years prior to the year which is supposed to be carried over to the year (hereinafter referred to as "foreign income tax carried over") exists, the foreign income tax carried over can be credited against income tax for the year, up to the amount of the remaining credit limit for income tax for the year.
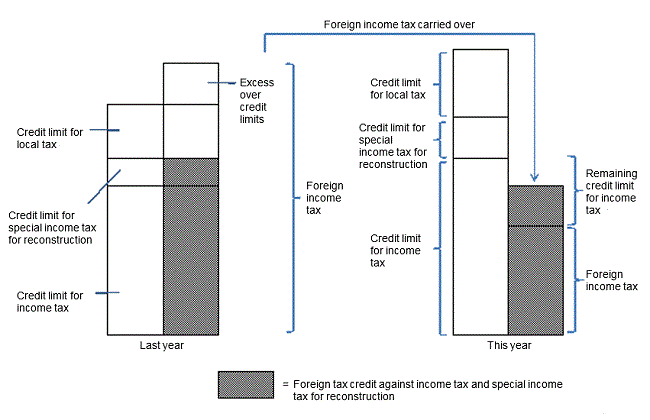
| (Note) “Foreign income tax carried over” is defined as the sum of the excess over credit limits for any of three years prior to the year, which should be appropriated to the remaining credit limit for income tax for the year if each of the excess over credit limits for any of three years prior to the year is to be appropriated to the remaining credit limit for income tax for the year in chronological order. |
6 Adjustment for changes in foreign income tax
(1) When foreign income tax is reduced
In the case where the amount of foreign income tax that a non-resident has been liable to pay is reduced in any of seven years following the year for which a foreign tax credit was applied to the non-resident with regard to the said amount of foreign income tax, the calculation of foreign tax credit for the year that includes the day on which the reduction in the said amount of foreign income tax takes place (hereinafter referred to as the “reduction year”) shall be as follows.
( ) ) |
The amount of foreign income tax for the reduction year shall be equal to the amount of foreign income tax that a resident becomes liable to pay in the reduction year (hereinafter referred to as the “amount of tax due”) minus the amount of the said reduction. |
( ) ) |
If there isn’t any amount of tax due in the reduction year or if the amount of tax due in the reduction year is smaller than the amount of the said reduction, all of the amount of the said reduction or the excess of the amount of the said reduction over the amount of tax due must be deducted from the excess over credit limits for any of three years prior to the reduction year. |
( ) ) |
If the amount of the said reduction still remains even after the adjustments as ( ) and ( ) and ( ) above, such remains must be included in the gross income of miscellaneous income for the reduction year. ) above, such remains must be included in the gross income of miscellaneous income for the reduction year. |
(2) When foreign income tax is increased
In the case where the amount of foreign income tax that a non-resident has been liable to pay is increased in any year following the year for which a foreign tax credit was applied to the non-resident with regard to the said amount of foreign income tax, it is deemed that the non-resident becomes newly liable for the increase in the said amount of foreign income tax in the year that includes the day on which the increase takes place, for the purpose of foreign tax credit’s calculation.
7 Procedure for applying foreign tax credit for non-residents
Adobe Reader is required to view PDF files. If you do not have Adobe Reader, please download it from the link above.
Foreign tax credit for non-residents shall apply only if a final tax return, amended return or request for correction (hereinafter referred to as "filing forms") is accompanied by the following documents. In this case, the amount of creditable foreign income tax, etc. shall be limited to the amount entered in the statement of (1) below as such amount, except for certain cases:
| (1) | “Detailed Statement for Foreign Tax Credit (for Non-residents)[外国税額控除に関する明細書(非居住者用)]” |
| (2) | Documents to certify the amount of foreign income tax to be imposed |
| (3) | A statement with a description of the following items: the name and the amount of tax imposed by foreign laws and regulations, the date on which the tax becomes due and the date or scheduled date of payment, the name of foreign (local) government which impose the foreign income tax, and an explanation that the foreign income tax falls upon the scope of creditable foreign income tax. |
| (4) |
In the case where the foreign income tax is reduced and 6(1) above is applied, a statement with a description of the following items: the reduction in the amount of foreign income tax, the date of reduction, and an explanation that the said amount of foreign income tax has been the basis of the calculation of the amount of tax credit for a certain year prior to the reduction year. |
| (5) |
A copy of the tax return which proves that the tax of (3) above is imposed, or an alternative document of such taxation, and documents to certify the payment of the tax if it has already been paid (such as a certificate of tax payment, notice of determination of correction, notice of determination of assessment, notification of tax payment and withholding record). |
| (6) |
Documents with a detailed description with regard to the calculation of the amount of foreign source income |
In addition, in the case where a non-resident has “credit limit carried over” or “foreign income tax carried over” as mentioned in 5 above, if the non-resident intends to credit it against the amount of income tax for the year, it is required to file "Detailed Statement for Foreign Tax Credit (for Non-residents)[外国税額控除に関する明細書(非居住者用)]" continuously, for every year from the oldest year of carry-over, with a description of the credit limit and foreign income tax to be paid for each year, along with filing forms. It is also required to state the amount to be credited by the carry-over in the filing forms for the year in which the foreign tax credit is applied for the non-resident by the carry-over, and attach "Detailed Statement for Foreign Tax Credit (for Non-residents)[外国税額控除に関する明細書(非居住者用)]."
The deductible amount of foreign tax credit is generally limited to the amount calculated based on credit limits for each year and the amount of foreign income tax that a non-resident becomes liable to pay in each year, which have been entered in “Detailed Statement for Foreign Tax Credit (for Non-residents) [外国税額控除に関する明細書(非居住者用)]” attached to filing forms for each year.
(Articles 165-2 and 165-6 of the Income Tax Act, Articles 292-2 and 292-7 through 292-14 of the Order for Enforcement of the Income Tax Act, Articles 66-8 and 66-9 of the Ordinance for Enforcement of the Income Tax Act, Articles 165-6-1 of the Fundamental Directives of Income Tax, Articles 13 and 14 of the Act on Special Measures for Securing Financial Resources Necessary for Reconstruction from the Great East Japan Earthquake, and Article 3 of the Ministerial Ordinance concerning Special Income Tax for Reconstruction)
- Consultation service for national tax is available at the Phone Consultation Center of the Regional Taxation Bureaus. Please take a look at “IF YOU NEED FURTHER INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT” and try the phone consultation service.